Revolutionizing Environmental Monitoring with Oil in Water Sensors

In recent years, environmental concerns have become a central focus of industries and governments worldwide. One of the most pressing issues is the contamination of water bodies by oil, which can have devastating effects on ecosystems and human health. Oil spills, runoff from industrial processes, and wastewater discharges can introduce harmful oils and hydrocarbons into rivers, lakes, oceans, and groundwater. The ability to monitor and detect oil in water quickly and accurately is essential to minimizing environmental damage and ensuring the safety of aquatic life.
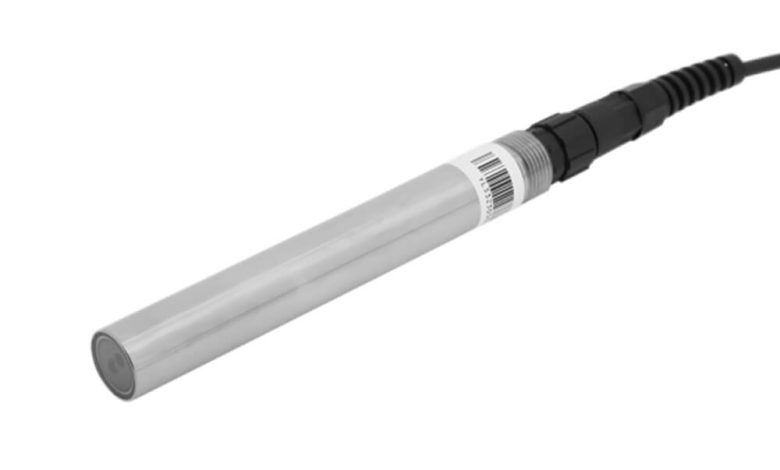
This is where Oil in water sensor come into play. These advanced sensors are designed to detect the presence of oil in water, allowing for real-time monitoring and rapid response to contamination. With the growing need for better environmental protection, oil in water sensors are revolutionizing the way industries and organizations monitor water quality. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of Oil in water sensor, how they work, and the impact they are having on environmental monitoring.
Understanding the Problem: Oil Contamination in Water
Oil contamination in water can originate from various sources, including industrial discharges, accidental spills, and runoff from land-based activities. Regardless of the source, the presence of oil in water is harmful to both the environment and public health. Oil forms a thin layer on the surface of water bodies, preventing the exchange of gases like oxygen. This disrupts the aquatic ecosystem, suffocating marine life and leading to the death of fish, birds, and other creatures that depend on the water for survival.
Additionally, oil contaminants can introduce toxic compounds into the water, leading to long-term ecological damage. Human populations relying on water bodies for drinking, fishing, and recreational activities are also at risk. The detection and removal of oil from water is therefore a priority for environmental agencies, industrial sectors, and conservation groups.
The Role of Oil in Water Sensors
Oil in water sensors are devices designed to measure the concentration of oil and other hydrocarbons in water. These sensors are widely used across various industries, including wastewater treatment, oil and gas, maritime, and environmental monitoring sectors. They help detect oil contamination in real-time, enabling immediate action to prevent further harm to ecosystems and human populations.
These sensors operate by utilizing different detection methods, depending on the technology used. Most modern oil in water sensors use either optical, electrochemical, or ultrasonic techniques to measure the presence of oil in water. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common sensor types and their working principles.
Types of Oil in Water Sensors
-
Optical Sensors
Optical sensors are based on the principle of light absorption or scattering by oil particles in water. These sensors work by passing light through the water sample and detecting changes in the light’s intensity as it interacts with oil molecules. When oil is present, it absorbs or scatters the light differently than water, and the sensor records this difference. Optical sensors are commonly used due to their high sensitivity and quick response times. They are particularly useful in detecting low concentrations of oil in water. -
Electrochemical Sensors
Electrochemical sensors detect oil in water by measuring the change in electrical properties, such as resistance or voltage, when oil molecules come into contact with the sensor’s electrode. As oil particles are non-polar, they can interact with the electrode material and produce a measurable signal. These sensors are often employed in environments where real-time monitoring is necessary, such as industrial wastewater treatment plants or offshore oil rigs. -
Ultrasonic Sensors
Ultrasonic sensors use sound waves to detect the presence of oil in water. These sensors work by emitting high-frequency sound waves into the water and measuring the time it takes for the waves to return. Since oil and water have different acoustic properties, the return time of the sound waves will differ based on the amount of oil present in the water. Ultrasonic sensors are often used in large-scale industrial applications and provide reliable, real-time data for monitoring oil contamination. -
Fluorescence-based Sensors
Fluorescence sensors detect oil by measuring the fluorescence emitted when oil molecules absorb light of a specific wavelength. The oil molecules then re-emit the light at a different wavelength, and the sensor measures this re-emission. These sensors are particularly effective at detecting aromatic hydrocarbons, which are often found in crude oil and other petroleum products.
Applications of Oil in Water Sensors
The application of oil in water sensors is widespread across many industries and sectors. Some of the key applications include:
1. Industrial Wastewater Treatment
Industries that use or produce oil-based substances, such as petroleum refineries, chemical manufacturers, and food processors, often discharge wastewater containing traces of oil. Oil in water sensors are used in these industries to monitor the oil content in wastewater effluents. This allows companies to ensure that their wastewater meets environmental standards and regulatory requirements before being discharged into natural water bodies.
2. Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas industry, offshore drilling rigs and oil platforms need to monitor the quality of the water around their operations. Oil spills and leaks can occur, and these sensors help detect and prevent larger-scale contamination. Oil in water sensors are integral in ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and minimizing environmental risks in oil exploration and extraction.
3. Maritime and Shipping
Oil spills in the ocean are a major environmental concern. To address this, oil in water sensors are used on ships, tankers, and maritime platforms to monitor oil levels in water. These sensors help in detecting oil leaks and preventing spills from reaching the open sea. Additionally, they are used in environmental monitoring stations along coastlines to track water quality and detect oil pollution early.
4. Environmental Monitoring and Research
Environmental agencies and research institutions use oil in water sensors to study the impact of oil contamination on ecosystems. These sensors help scientists track the movement and concentration of oil in natural water bodies, enabling them to assess the extent of environmental damage caused by spills or runoff. They are also used in long-term water quality monitoring programs to ensure the health of aquatic environments.
The Benefits of Oil in Water Sensors
The implementation of oil in water sensors offers several benefits, both for businesses and the environment. Some of the key advantages include:
-
Real-Time Monitoring: Oil in water sensors provide real-time data on water quality, enabling immediate action to be taken in case of oil contamination. This can prevent larger environmental disasters and reduce response time in critical situations.
-
Cost-Effective and Efficient: By detecting oil contamination early, these sensors help industries avoid costly fines and remediation efforts. They also allow companies to optimize their treatment processes by identifying areas where oil discharge can be reduced.
-
Environmental Protection: By preventing oil from reaching water bodies, these sensors play a crucial role in protecting ecosystems and wildlife. They help mitigate the environmental impact of industrial activities and reduce the risks associated with oil spills.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Many countries have strict regulations regarding the discharge of oil and other pollutants into water. Oil in water sensors help industries comply with these regulations, avoiding penalties and ensuring environmental responsibility.
Conclusion
Oil in water sensors have revolutionized environmental monitoring by providing an efficient, reliable, and real-time method of detecting oil contamination in water. With their ability to provide early detection, enhance response times, and support environmental protection efforts, these sensors are essential tools for industries and agencies involved in water quality management. As the global demand for cleaner water and healthier ecosystems continues to rise, the role of oil in water sensors will only become more crucial in ensuring a sustainable future for our planet’s water resources.